LEDs Turned into Optical WLAN
August 1st, 2011Data Traveling by Light
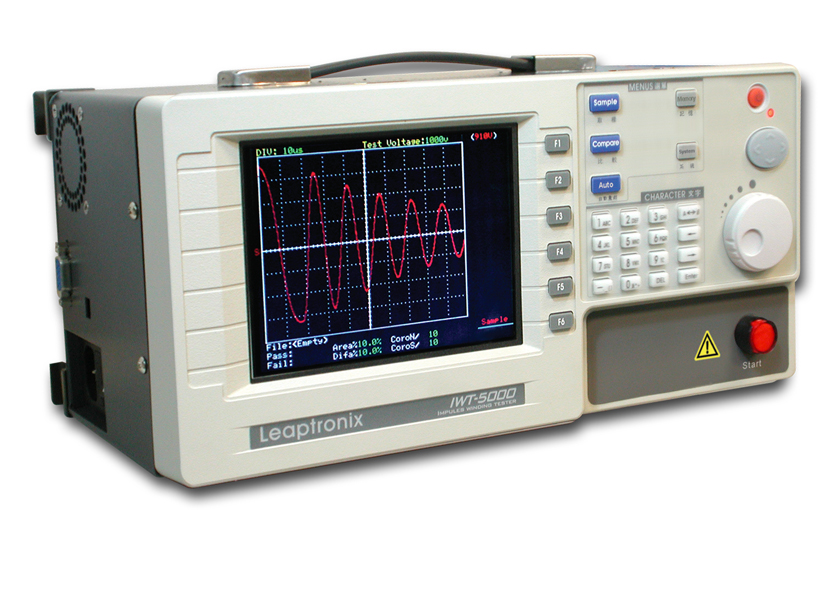
Regular LEDs can be turned into optical WLAN with only a few additional components thanks to visible light communication (in short, VLC). The lights are then not just lighting up, they also transfer data. They send films in HD quality to your iPhone or laptop, with no loss in quality, quickly and safely.
 Just imagine the following scenario: four people are comfortably ensconced in a room. Each one of them can watch a film from the Internet on his or her laptop, in HD quality. This is made possible thanks to optical WLAN. Light from the LEDs in the overhead lights serves as the transfer medium. For a long time, this was just a vision for the future. However, since scientists from the Fraunhofer Institute for Telecommunications, Heinrich Hertz Institute HHI in Berlin, Germany, have developed a new transfer technology for video data within the scope of the OMEGA project of the EU, its implementation in real life is getting markedly closer. At the end of May, the scientists were able to present the results of the project in Rennes, France. They were able to transfer data at a rate of 100 megabits per second (Mbit/s) without any losses, using LEDs in the ceiling that light up more than ten square meters (90 square feet). The receiver can be placed anywhere within this radius, which is currently the maximum range. “This means that we transferred four videos in HD quality to four different laptops at the same time,“ says Dr. Anagnostis Paraskevopoulos from the HHI.
Just imagine the following scenario: four people are comfortably ensconced in a room. Each one of them can watch a film from the Internet on his or her laptop, in HD quality. This is made possible thanks to optical WLAN. Light from the LEDs in the overhead lights serves as the transfer medium. For a long time, this was just a vision for the future. However, since scientists from the Fraunhofer Institute for Telecommunications, Heinrich Hertz Institute HHI in Berlin, Germany, have developed a new transfer technology for video data within the scope of the OMEGA project of the EU, its implementation in real life is getting markedly closer. At the end of May, the scientists were able to present the results of the project in Rennes, France. They were able to transfer data at a rate of 100 megabits per second (Mbit/s) without any losses, using LEDs in the ceiling that light up more than ten square meters (90 square feet). The receiver can be placed anywhere within this radius, which is currently the maximum range. “This means that we transferred four videos in HD quality to four different laptops at the same time,“ says Dr. Anagnostis Paraskevopoulos from the HHI.
“The fundamentals of visible light communication (VLC) were developed together with the industry partners Siemens and France Telecom Orange Labs,“ said the expert. At HHI, the team of project manager Klaus-Dieter Langer is now further developing the new technology. “For VLC the sources of light – in this case, white-light LEDs – provide lighting for the room at the same time they transfer information. With the aid of a special component, the modulator, we turn the LEDs off and on in very rapid succession and transfer the information as ones and zeros. The modulation of the light is imperceptible to the human eye. A simple photo diode on the laptop acts as a receiver. As Klaus-Dieter Langer explains, “The diode catches the light, electronics decode the information and translate it into electrical impulses, meaning the language of the computer.“ One advantage is that it takes only a few components to prepare the LEDs so that they function as transfer media. One disadvantage is that as soon as something gets between the light and the photo diode (for example, when someone holds his hand over the diode) the transfer is impaired. Laptops, Palm devices or mobile telephones are all potential end devices.
The scientists emphasize that VLC is not intended to replace regular WLAN, PowerLAN or UMTS. It is best suited as an additional option for data transfer where radio transmission networks are not desired or not possible – without needing new cables or equipment in the house. Combinations are also possible, such as optical WLAN in one direction and PowerLAN for the return channel. Films can be transferred to the PC like this and also played there, or they can be sent on to another computer.
The new transmission technology is suitable for hospitals, for example, because radio transmissions are not allowed there. Despite this fact, high data rates must be transmitted without losses and unzipped, according to the experts. If part of the communication occurs via the light in the surgical room, this would make it possible to control wireless surgical robots or transmit x-ray images. In airplanes, each passenger could view his own
entertainment program on a display, saving aircraft manufacturers miles of cables. Another possible venue for the application of this technology are production facilities, where radio transmissions very often interfere with the processes.
Currently the scientists are developing their systems toward higher bit rates. “Using red-blue-green-white light LEDs, we were able to transmit 800 Mbit/s in the lab,“ said Klaus-Dieter Langer. “That is a world record for the
VLC method.“ The HHI scientists will showcase how videos are transmitted by light in Hall 11.1, Booth 8 at the International Telecommunications Fair IFA (Internationale Funkausstellung IFA) in Berlin from September 2-7, 2011. (source www.fraunhofer.de)


 LEXINGTON — As part of the Patrick-Murray Administration’s nation-leading commitment to clean energy, Massachusetts Energy and Environmental Affairs (EEA) Secretary Richard K. Sullivan Jr. today took the Commonwealth’s clean energy revolution to Lexington’s Battle Green to announce the award of 105 electric vehicle charging stations for 25 cities and towns across the state.
LEXINGTON — As part of the Patrick-Murray Administration’s nation-leading commitment to clean energy, Massachusetts Energy and Environmental Affairs (EEA) Secretary Richard K. Sullivan Jr. today took the Commonwealth’s clean energy revolution to Lexington’s Battle Green to announce the award of 105 electric vehicle charging stations for 25 cities and towns across the state. The Commonwealth will also be installing additional charging stations, separate from these municipal installations, at Logan Airport garages, Logan Express parking lots and at MBTA commuter parking locations.
The Commonwealth will also be installing additional charging stations, separate from these municipal installations, at Logan Airport garages, Logan Express parking lots and at MBTA commuter parking locations.
 ORLANDO, Fla., – The U.S. Air Force has approved Northrop Grumman Corporation’s Theater Deployable Communications (TDC) Wireless Distribution Module (WDM) for production.
ORLANDO, Fla., – The U.S. Air Force has approved Northrop Grumman Corporation’s Theater Deployable Communications (TDC) Wireless Distribution Module (WDM) for production.
 Researchers from the University of California at Riverside in collaboration with a team from the University of Central Florida have figured out a way to increase the use of ultraviolet semiconductor diode lasers. These tiny lasers, less than the width of a hair strand, are already widely used in data processing, information storage and biology.
Researchers from the University of California at Riverside in collaboration with a team from the University of Central Florida have figured out a way to increase the use of ultraviolet semiconductor diode lasers. These tiny lasers, less than the width of a hair strand, are already widely used in data processing, information storage and biology. By combining advanced laser technologies in a new way, physicists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have generated microwave signals that are more pure and stable than those from conventional electronic sources. The apparatus could improve signal stability and resolution in radar, communications and navigation systems, and certain types of atomic clocks.
By combining advanced laser technologies in a new way, physicists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have generated microwave signals that are more pure and stable than those from conventional electronic sources. The apparatus could improve signal stability and resolution in radar, communications and navigation systems, and certain types of atomic clocks. Aimed at building the necessary transmission infrastructure and developing and deploying digital information or “smart grid” technologies, these initiatives will facilitate the integration of renewable sources of electricity into the grid; accommodate a growing number of electric vehicles on America’s roads; help avoid blackouts and restore power quicker when outages occur; and reduce the need for new power plants.
Aimed at building the necessary transmission infrastructure and developing and deploying digital information or “smart grid” technologies, these initiatives will facilitate the integration of renewable sources of electricity into the grid; accommodate a growing number of electric vehicles on America’s roads; help avoid blackouts and restore power quicker when outages occur; and reduce the need for new power plants.